Define thr Algae in plant kingdom
Algae are chlorophyll-bearing, simple, thalloid, autotrophic and largely aquatic organisms found in both fresh water and marine. They are found in many other habitats such as moist stones, soil and wood. Some of them also occur with fungi (lichens) and animals. The form and size of algae is highly variable, Algae are ranging from colonial forms and filamentous forms . A few of the marine forms such as kelps, forms massive plant bodies.
The algae reproduce by vegetative, asexual and sexual methods.
Vegetative reproduction is by fragmentation. Each fragment develops into a thallus.
Asexual reproduction is by the production of different types of spores, the most common being the zoospores. They are flagellated (motile) and on germination gives rise to new plants.
Sexual reproduction takes place through fusion of two gametes. These gametes can be flagellated and similar in size (as in Ulothrix) or non-flagellated (non-motile) but similar in size (as in Spirogyra). Such reproduction is called isogamous. Fusion of two gametes dissimilar in size, as in species of Eudorina is termed as anisogamous. Fusion between one large, nonmotile(static) female gamete and a smaller, motile male gamete is termed oogamous, examples are Volvox, Fucus.
Divisions of Algae and their Main Characteristics
| Classes | Common Name | MajorPigments | Stored Food | Cell Wall | Flagellar Number and position of Insertions | Habitat | Picture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorophyceae | Green algae | Chlorophyll a, b | Starch | Cellulose | 2-8, equal, apical | Fresh water, brackish water, salt water | 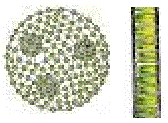 |
| Phaeophyceae | Brown algae | Chlorophyll a, c fucoxanthin | Mannitol, laminarin | Cellulose and algin | 2, algae lateral | Fresh water (rare) brackish water, salt water | 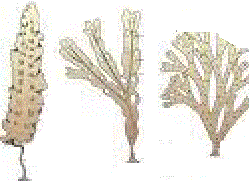 |
| Rhodophyceae | Red algae | Chlorophyll a, d, phycoerythrin | Floridean starch | Cellulose, pectin and poly sulphate esters | Absent | Fresh water(some), brackish water, salt water (most) |  |
