Plant Life Cycles and alternation of generation
Alternation of generations is common in plants, algae, and fungi. In plants both haploid and diploid cells can divide by mitosis. This ability leads to the formation of different plant bodies is due to haploid and diploid. The haploid plant body produces gametes by mitosis. This plant body represents a gametophyte.
Following fertilisation the zygote also divides by mitosis to produce a diploid sporophytic plant body. Haploid spores are produced by this plant body by meiosis. These in turn, divide by mitosis to form a haploid plant body once again. Therefore during the life cycle of any sexually reproducing plant there is an alternation of generations between gamete producing haploid gametophyte and spore producing diploid sporophyte.
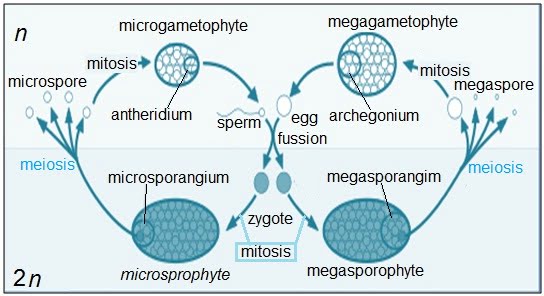
Stages in alternation of generations cycle
1. The diploid sporophyte has a structure called sporangium.
2. The sporangium undergoes meiosis and forms haploid spores.
3. The spore develops into a gametophyte which is haploid in nature.
4. The gametophyte has the reproductive organs which undergo mitosis to form haploid gametes.
5. The gametes fertilize to form a haploid zygote which matures into a mature sporophyte.
