Define the Bryophytes in plant kingdom
Bryophytes are plants that can live in soil but depend on water for sexual reproduction. Their plant body is more differentiated than that of algae. Bryophytes include the various mosses and liverworts that are found commonly growing in moist shaded areas in the hills. They play an important role in plant succession on bare rocks/soil.
It is thallus-like and prostrate and attached to the base by rhizoids. They have root-like, leaf-like and stem-like structures. Bryophytes are divided into liverworts and mosses. The plant body of liverworts is thalloid and dorsiventral whereas mosses have straight, slender axes with spirally arranged leaves. The main plant body of the bryophyte is the gamete-producer and is called the gametophyte. The sex organs in bryophytes are multicellular.
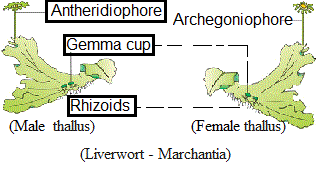
It consists of male sex organs called antheridia produce biflagellate antherozoids and female sex organs called archegonia is flash-shaped and produces a single egg.
The antherozoids are released into water where they come in contact with archegonium. An antherozoid fuses with the egg to produce the zygote. (Male and female gametes fuse to form the zygote which produces a multicellular body called a sporophyte.) It produces haploid spores. The spores germinate to form the gametophyte.
They were mainly based on botanical traits or the androecium structure (the system given by Linnaeus). Such systems were artificial, separating closely related species because they were based on certain characteristics. Artificial systems that gave equal importance to vegetative and sexual characteristics is not acceptable because we know that often vegetative traits are more easily influenced by the environment. In contrast, natural classification systems evolved, which were based on natural similarities between organisms and consider.
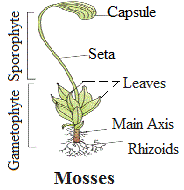
Sporophyte characteristics of bryophytes
| Liverworts | Mosses | Hornworts | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capsule form | Simple | Differentiated (operculum, peristome) | Elongated |
| Columella | Absent | Present | Present |
| Dehiscence | Longitudinal or irregular | Transverse | Longitudinal |
| Dispersion of spores | Elaters | Peristome teeth | Pseudo-elaters |
| Growth | Defined | Defined | Continuous |
| Maturation of spores | Simultaneous | Simultaneous | Graduate |
| Persistence | Ephemeral | Persistent | Persistent |
| Seta | Present | Present | Absent |
| Stomata | Absent | Present | Present |
| Structure | Small, without chlorophyll | Large, with chlorophyll | Large, with chlorophyll |
