The Parallel Plate Capacitor
There are two very small and thin conducting plates placed parallel to each other at a fine distance lets suppose it as d. Two plates must be separated through a medium.
So air, glass, paper etc are used as medium inside these conductors. In these conductors connection of one plate is done with earth and other plate is an insulated plate. When two parallel plates are connected across a battery, the plates will become charged and an electric field will be established between them
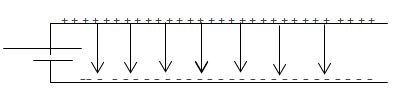
Remember that the direction of an electric field is defined as the direction that a positive test charge would move. So in this case, the electric field would point from the positive plate to the negative plate. Since the field lines are parallel to each other, this type of electric field is uniform and is calculated with the equation E = V/d .
Note that the electric field strength, E, can be measured in either the units V/m, or equivalently, N/C.
[E] = V/d
(J/C)/m
(Nm)/C/ m
N/C
Since the field lines are parallel and the electric field is uniform between two parallel plates, a test charge would experience the same force of attraction or repulsion no matter where it is located. That force is calculated with the equation F = qE. To review more about electric fields between parallel plates, go back and review this resource lesson.
