Capacitors and Capacitance
Capacitor
The capacitor is a two-terminal electrical device that possesses the ability to store energy in the form of an electric charge. The capacitor is consists of two electrical conductors that are separated by a distance.
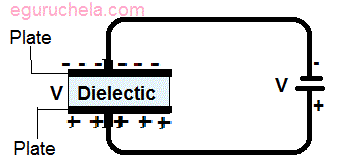
The space between the conductors may be filled by vacuum or with an insulating material known as a dielectric and The ability of the capacitor to store charges is called capacitance.
Capacitance
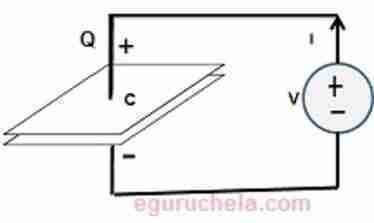
Capacitance is typified by a parallel plate arrangement and is defined in terms of charge storage
Capacitance is the ability of a body to store an electrical charge.
A material with a large capacitance holds more electric charge at a given voltage, than one with low capacitance.
Any object that can be electrically charged exhibits capacitance, however the concept is particularly important for understanding the operations of the capacitor, one of the three fundamental electronic components
C = Q / V
Unit = coulomb/volt = Fared
Where Q is the magnitude of the charge stored on each plate
and voltage applied to the plate
Factors affecting capacitance
Dielectric: Dielectric effect on capacitance is that the greater the permittivity of the dielectric the greater the capacitance, similarly lesser the permittivity of the dielectric the lesser is the capacitance.
Some materials offer less opposition to the field flux for a given amount of field force. Materials with higher permittivity allow more field flux thats why greater charge is collected.
Plate spacing: Plate spacing effect on the capacitance is that it is inversely proportional to the distance between the plates. It is represented as:
C ∝ 1/d
Area of the plates: Area of the plate effect, the capacitance is directly proportional to the area. Bigger the plate area grts higher capacitance value. It is represented as:
C ∝ A
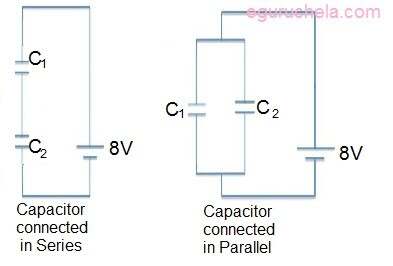
Capacitor connected in Series
The total capacitance of the capacitors connected in series C1, C2, C3,.... :
1/CTotal = 1/C1 + 1/C2 + 1/C3 + ...
Capacitor connected in Parallel
The total capacitance of the capacitors connected in parallel C1, C2, C3,.. :
CTotal = C1+C2+C3+...
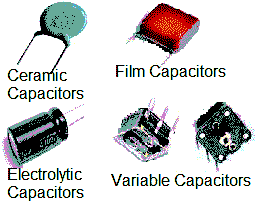
Types of Capacitors
Ceramic Capacitors: The ceramic capacitors uses ceramic as the dielectric material and used for high-frequency circuits such as audio to RF. It can develop high capacitance or low capacitance by altering the thickness of the ceramic disc.
Film Capacitors: The film capacitors uses plastic film as the dielectric medium and available up to 1500 volts. There are two types of film condensers( radial type lead and axial type lead).
Electrolytic Capacitors: The electrolytic uses the oxide layer as the dielectric material haviing wide tolerance capacity. There are two types of electrolytic capacitors(tantalum and aluminum).
Electrolytic capacitors are available with working voltages of up to approximately 500V.
Variable capacitor: The variable capacitors uses air as the dielectric medium. The variable capacitor is one whose capacitance can be mechanically adjusted several times.
Applications of capacitor
1. Energy storage.
2. Power conditioning.
3. Power factor correction Capacitors.
4. RF coupling and decoupling applications.
5. Smoothing capacitor applications.
6. Hold-up capacitor applications.
7. Capacitors as Sensors.
