Basic Properties of Electric Charge
Electric charge is a physical property of mater that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter.
There are two types of electric charges namely, namely positive and negative and their effect tend to cancel each other.
The phenomena of two objects sticking together can be explained by the notion that objects when rubbed can gain a net electric charge.
There are two types of charge, labeled positive ( + ) and negative ( - ), with the following basic property:
- Like charges of the same sign repel each other.
- Unlike charges of the opposite sign attract each other.
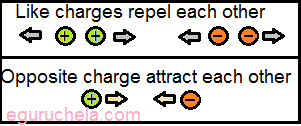
Kinds of charges
1. Negative charge
Electrons are negatively charged particles and protons, of which nucleus is made of, are positively charged particles. Actually nucleus is made of protons and neutrons but neutrons are uncharged particles.
2. Positive charge
Electric force between two electrons is same as electric force between two protons kept at same distance apart i. e., both set repel each other but electric force between an electron and proton placed at same distance apart is not repulsive but attractive in nature.
Basic properties of electric charge
The basic properties of electric charges are as follows:
Charges are additive in nature
Charge is a conserved quantity
Quantization of charge
Additive property of electric charge
The electric charges are additive in nature having a scalar property and it depends upon the type of electric charge they carry.
It is possible to add them directly. e.g. let's consider a system containing only two charges q1 and q2.
According to this property, the total charge of the system can be calculated by algebraic sum of q1 and q2 means Q = q1 + q2.
Similarly now, a system contains q1, q2, q3, q4 - - - qn, then the net charge(Q) of the whole system can be :
Net Charge = q1 + q2 + q3 + q4 + - - - + qn
Conservative nature of electric charge
The electric charge of a particle is conservative in nature means that the charge can neither be created nor be destroyed.
The charges can be transferred from one system to another system by the mechanism like conduction and induction.
Conservative nature is similar to the law of conservation of mass and similar to the first law of thermodynamics (law of conservation of energy).
The Rubbing of two bodies involves a transfer of electrons from one body to another.
Quantization of Charge
The charge of a system is a fixed quantity means technically say that charge is a quantized quantity.
The net charge of a system can be expressed as the integral multiples of the basic unit of charge.
In 1912, The principle of the quantization of electric charge was first proposed by English scientist Faraday.
This proposal was based on his experimental laws of electrolysis and later this principle was demonstrated and proved by Millikan.
