Reverse osmosis
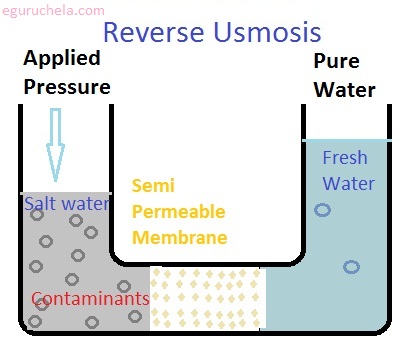
It is a water purification technology that uses a semipermeable membrane to remove ions,molecules, and larger particles from drinking water. In reverse osmosis, an applied pressure is used to overcome osmotic pressure, a colligative property, that is driven by chemical potential differences of the solvent, athermodynamic parameter.
As water passes through the membrane to the salt solution, the level of liquid in the saltwater compartment will rise until enough pressure, caused by the difference in levels between the two compartments, is generated to stop the osmosis.
Reverse Osmosis
Working-->
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Osmosis is a special case of diffusion in which the molecules are water and the concentration gradient occurs across a semipermeable membrane. The semipermeable membrane allows the passage of water, but not ions or larger molecules.
Benefits
Low salt passage, typically > 99,7% at standard conditions in brackish water
High flow productivity
Improved barrier layer chemistry (lower charge and higher cross-linkage) providing lower membrane fouling rates.
Go to index page
