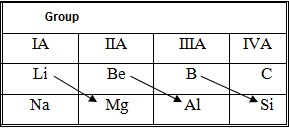
Diagonal relationship
A diagonal relationship is said to exist between certain pairs of diagonally adjacent elements in the second and third periods of theperiodic table. These pairs (lithium (Li) and magnesium (Mg), beryllium (Be) and aluminium (Al), boron (B) and silicon (Si) etc.) exhibit similar properties; for example, boron and silicon are both semiconductors, forming halides that are hydrolysed in water and have acidic oxides. Diagonal relationships occur because of the directions in the trends of various properties as you move across or down the periodic table. Many of the chemical properties of an element are related to the size of the atom.
Similarities between Lithium and magnesium: