The Ribosomes
In 1953, George Palade observed as dense particles using electron microscope, the ribosomes shows granular structures. They are composed of ribonucleic acid (RNA) and proteins and are not surrounded by any membrane.
The eukaryotic ribosomes are 80S while the prokaryotic ribosomes are 70S.
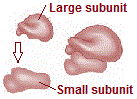
Each ribosome has two subunits as follows:
The two subunits of 80S ribosomes are 60S and 40S while that of 70S ribosomes are 50S and 30S.
The ‘S’ (Svedberg’s Unit) stands for the sedimentation coefficient (it is indirectly a measure of density and size).
Both 70S and 80S ribosomes are composed of two subunits.
Around 62% of ribosomes are comprised of RNA, while the rest is proteins.
General Definition
Ribosomes are most important cell organelles composed of RNA and protein that converts genetic code into chains of amino acids.
Important function of ribosome
The proteins synthesized in the cytoplasm are utilized in the cytoplasm itself.
Ribosome assembles amino acid to form proteins that are essential to carry out cellular functions.
The DNA produces mRNA by the process of DNA transcription.
The mRNA is synthesized in the nucleus and transported to the cytoplasm for the process of protein synthesis.
The ribosomal subunits in the cytoplasm are bound around mRNA polymers. The tRNA then synthesizes proteins.
