The eukaryotic cells
The eukaryotes include all the protists, plants, animals and fungi. In eukaryotic cells there is an extensive compartmentalisation of cytoplasm through the presence of membrane bound organelles. All the eukaryotic cells are not identical.
Eukaryotic cells possess an organised nucleus with a nuclear envelope. In addition eukaryotic cells have a variety of complex locomotory and cytoskeletal structures.
Their genetic material is organised into chromosomes.
The Plant and animal cells are different as the former possess cell walls, plastids and a large central vacuole which are absent in animal cells. On the other hand, animal cells have centrioles which are absent in almost all plant cells.
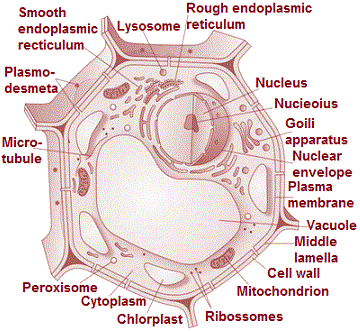
(Plant cell)

(Animal cell)
Features of Eukaryotic Cells
The details of individual cell organelles with their structure and functions.
The structure and functions
Plasma membrane
Plasma membrane comprises specific embedded proteins, which help in the exchange of substances in and out of the cell. It separates the cell from the outside environment.
The Cell wall
Cell wall is composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, pectins, proteins, etc. It is a rigid structure present outside the plant cell. It is absent in animal cells. It is a protective layer that protects the cell from any injury or pathogen attacks.
Cell wall provides shape to the cell and helps in cell-to-cell interaction.
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is present inside the cytoplasm, which consists of microfilaments, microtubules, and fibres to provide perfect shape to the cell, anchor the organelles, and stimulate the cell movement.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum is a network of small, tubular structures that divides the cell surface into two parts: luminal and extraluminal.
Endoplasmic Reticulum is of two types as follows:
1. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum contains ribosomes.
2. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum that lacks ribosomes and is therefore smooth.
Nucleus
The nucleoplasm enclosed within the nucleus contains DNA and proteins. The nuclear envelop consists of two layers (outer membrane and inner membrane).
Both the membranes are permeable to ions, molecules, and RNA material. Ribosome production also takes place inside the nucleus.
Golgi Apparatus
Golgi apparatu is made up of flat disc-shaped structures called cisternae. It is absent in red blood cells of humans and sieve cells of plants. Golgi Apparatus are arranged parallel and concentrically near the nucleus and It is an important site for the formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids.
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are the main site for protein synthesis and are composed of proteins and ribonucleic acids.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are the powerhouse of cells because they produce energy. It consists of an outer membrane and an inner membrane. The inner membrane is divided into folds called cristae. Mitochondria help in the regulation of cell metabolism.
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are suicidal bags because they possess hydrolytic enzymes to digest protein, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids.
Plastids
Plastids are double-membraned structures and are found only in plant cells. The plastids are three types as follows:
1. Chloroplast that contains chlorophyll and is involved in photosynthesis.
2. Chromoplast that contains a pigment called carotene that provides the plants yellow, red or orange colours.
3. Leucoplasts that are colourless and store oil, fats, carbohydrates or proteins.
Examples of Eukaryotic Cells
Plant Cells
The plant cell wall is made up of cellulose, which provides support to the plant. It has a large vacuole which maintains the turgor pressure. The plant cell contains chloroplast which aids in the process of photosynthesis.
Fungal Cells
The fungal cell wall is made of chitin. Some fungi have holes known as septa which allow the organelles and cytoplasm to pass through them.
Animal Cells
Animal Cells do not have cell walls. Instead, they have a cell membrane. That is why animals have varied shapes. They have the ability to perform phagocytosis and pinocytosis.
Protozoa
Protozoans are unicellular organisms. Some protozoa have cilia for locomotion. A thin layer called pellicle provides supports to the cell.
