The morphology of Frog
The frog is a chordate, having characteristics of the Phylum Chordata. The frogs have bilateral symmetry. Frogs are amphibian means "both lives", The frogs start their lives in the water and then live on land.
The body of the frog is divisible into head and trunk. Neck and tail are absent in a frog.
The skin of frog is smooth and slippery due to the presence of mucus. The skin is always maintained in a moist condition.
The colour of dorsal side of body is generally olive green with dark irregular spots. On the ventral side the skin is uniformly pale yellow.
The frog never drinks water but absorb it through the skin. Body of a frog is divisible into head and trunk.
A neck and tail are absent. Above the mouth, a pair of nostrils is present.
The eyes are bulged and covered by a nictitating membrane that protects them while in water.
On either side of eyes a membranous tympanum (ear) receives sound signals.
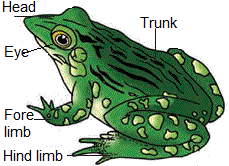
The forelimbs and hind limbs help in swimming, walking, leaping and burrowing.
The hind limbs end in five digits and they are larger and muscular than fore limbs that end in four digits.
Feet have webbed digits that help in swimming.
Frogs exhibit sexual dimorphism. Male frogs can be distinguished by the presence of sound producing vocal sacs and also a copulatory pad on the first digit of the fore limbs which are absent in female frogs.
life cycle of a frog
It includes three stages: Egg, larva and adult
