Structural Organisation in Animal
The levels of structural organization in animals, are made up of four levels of organization as follows:
Cells → Tissues → Organs → Organ system
It is large variety of organisms (unicellular and multicellular) of the animal kingdom.
In unicellular organisms all functions like digestion, respiration and reproduction are performed by a single cell.
In the complex body of multicellular animals the same basic functions are carried out by different groups of cells in a well organised manner.
The body of a simple organism like Hydra is made of different types of cells and the number of cells in each type can be in thousands.
The human body is composed of billions of cells to perform various functions.
In multicellular animals, a group of similar cells alongwith intercellular substances perform a specific function. Such an organisation is called tissue.
Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems split up the work in a way that ensures the survival of the body as a whole and exhibit division of labour. A tissue is defined as group of cells along with intercellular substances performing one or more functions in the body.
Epithelia are sheet like tissues lining the bodys surface and its cavities, ducts and tubes. Epithelia have one free surface facing a body fluid or the outside environment. Their cells are structurally and functionally connected at junctions.
Diverse types of connective tissues bind together, support, strengthen, protect, and insulate other tissue in the body.
Soft connective tissues consist of protein fibres as well as a variety of cells arranged in a ground substance. Cartilage, bone, blood, and adipose tissue are specialised connective tissues.
Cartilage and bone are both structural materials.
Blood is a fluid tissue with transport functions. Adipose tissue is a reservoir of stored energy. Muscle tissue, which can contract (shorten) in response to stimulation, helps in movement of the body and specific body parts.
Skeletal muscle is the muscle tissue attached to bones. Smooth muscle is a component of internal organs.
Cardiac muscle makes up the contractile walls of the heart.
Connective tissue covers all three types of tissues.
List of tissues, origin and functions
| Tissue | Origin | Function | Figure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epithelial | Ecto, Meso and Endoderm | Protection, absorption and secretion | 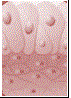 |
| Connective | Mesodermal | Connect, support and transport | 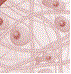 |
| Muscular | Mesodermal | Locomotion and movement | 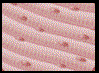 |
| Neural | Ectodermal | Control and coordination | 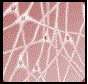 |
