The morphology of cockroch
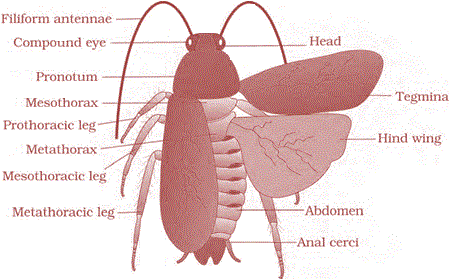
Cockroaches are brown or black bodied animals that are included in class Insecta of Phylum Arthropoda and cockroach has bilateral symmetry.
Bright yellow, red and green coloured cockroaches have also been reported in tropical regions. Their size ranges from ¼ inches to 3 inches (0.6-7.6 cm) and have long antenna, legs and flat extension of the upper body wall that conceals head.
They are nocturnal omnivores that live in damp places throughout the world. They have become residents of human homes and thus are serious pests and vectors of several diseases.
The adults of the common species of cockroach, Periplaneta americana are about 34-53 mm long with wings that extend beyond the tip of the abdomen in males.
The body of the cockroach is segmented and divisible into three distinct regions as follows:
The entire body is covered by a hard chitinous exoskeleton. In each segment, exoskeleton has hardened plates called sclerites that are joined to each other by a thin and flexible articular membrane.
The exoskeleton is composed of a thin, outer protein layer, the epicuticle, and a thick inner chitin–protein layer, the procuticle.
Head
Head is triangular in shape and lies anteriorly at right angles to the longitudinal body axis. It is formed by the fusion of six segments and shows great mobility in all directions due to flexible neck. The head capsule bears a pair of compound eyes. A pair of thread like antennae arise from membranous sockets lying in front of eyes.
Antennae have sensory receptors that help in monitoring the environment. Anterior end of the head bears appendages forming biting and chewing type of mouth parts.
The cockroaches do have a sense of smell, Cockroaches communicate through pheromones, allowing them to transmit a variety of intentions, messages, and suggestions. They can warn others that danger is nearby, suggest good food sources, encourage mating, and invite other roaches to a good shelter.
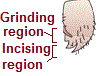
The mouthparts consisting of a labrum (upper lip), a pair of mandibles, a pair of maxillae and a labium (lower lip). A median flexible lobe, acting as tongue (hypopharynx), lies within the cavity enclosed by the mouthparts.
| Labrum | Mandibles | Maxillae | Labium | Hypopharynx |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Thorax
Thorax consists of three parts as follows:
The head is connected with thorax by a short extension of the prothorax known as the neck. Each thoracic segment bears a pair of walking legs.
The first pair of wings arises from mesothorax and the second pair from metathorax.
Forewings (mesothoracic) called tegmina are opaque dark and leathery and cover the hind wings when at rest. The hind wings are transparent, membranous and are used in flight.
Abdomen
The abdomen in both males and females consists of 10 segments.
In the case of females, the 7th sternum is boat shaped and together with the 8th and 9th sterna forms a brood or genital pouch whose anterior part contains female gonopore, spermathecal pores and collateral glands.
In the case of males, genital pouch or chamber lies at the hind end of abdomen bounded dorsally by 9th and 10th terga and ventrally by the 9th sternum.
It contains dorsal anus, ventral male genital pore and gonapophysis. Males bear a pair of short, threadlike anal styles which are absent in females.
In both sexes, the 10th segment bears a pair of jointed filamentous structures called anal cerci.
