Anatomy - The plant tissues
The collection of cells usually performing a common function is called tissue. Plant tissues can be grouped into plant tissue systems each performing specialized functions. A plant tissue system is defined as a functional unit, connecting all organs of a plant. Plant tissue system is also grouped into various tissues based on their functions.
Tissues are classified into two main groups called meristematic and permanent tissues based on whether the cells being formed are capable of dividing or not.
Merismatic tissues
Growth in plants is largely restricted to specialised regions of active cell division called meristems.
It consist of a group of cells that have the ability to divide. Plants have different kinds of meristems. The meristems which occur at the tips of roots and shoots and produce primary tissues are called apical meristems .
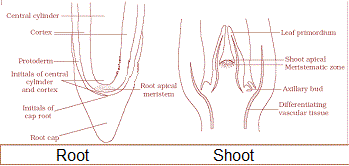
Root apical meristem occupies the tip of a root while the shoot apical meristem occupies the distant most region of the stem axis.
During the formation of leaves and elongation of stem, some cells left-behind from shoot apical meristem, constitute the axillary bud. Such buds are present in the axils of leaves and are capable of forming a branch or a flower.
The meristem which occurs between mature tissues is known as intercalary meristem. They occur in grasses and regenerate parts removed by the grazing herbivores.
Both apical meristems and intercalary meristems are primary meristems because they appear early in life of a plant and contribute to the formation of the primary plant body.
The meristem that occurs in the mature regions of roots and shoots of many plants, particularly those that produce woody axis and appear later than primary meristem is called the secondary meristem or lateral meristem.
These tissues are small, cuboidal, densely packed cells which keep dividing to form new cells. These tissues are capable of stretching, enlarging and differentiating into other types of tissues as they mature. Meristematic tissues give rise to permanent tissues. Merismatic tissues can be of three types depending on the region where they are present (Apical meristems, lateral meristems, and intercalary meristems).
Permanent tissues
Is forms the major portion of the plant. They are derived from the merismatic tissues and have lost their ability to divide. They have attained their mature form. They are further classified into two types: Simple and complex permanent tissues.
Simple Permanent tissues
| Parenchyma | These tissues are found in the soft parts of a plant such as the roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. The cells of this tissue are loosely packed and contain large intercellular spaces between them. Each cell has a vacuole at the center. The functions of parenchyma tissues are storage, photosynthesis, and to help the plant float on water. | 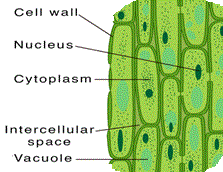 |
| Collenchyma | Are similar to parenchyma cells with thicker cell walls. They are meant to provide mechanical support to the plant structure in parts such as petiole of the leaf. | 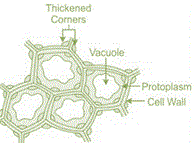 |
| Sclerenchyma | The cells of this tissue are dead. They are rigid, contain thick and lignified secondary walls. Their main function is to provide strength and support to parts of the plant. | 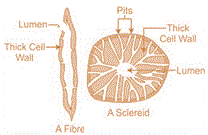 |
Complex Permanent Tissue
Unlike simple permanent cells which look the same and are made up of one type of cells, complex permanent tissues are made up of more than one type of cells. These different types of cells coordinate to perform a function. Xylem and Phloem are complex permanent tissues and are found in the vascular bundles in the plants.
| Xylem | It consists of tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres. Tracheids and vessels are hollow tube-like structures that help in conducting water and minerals. The xylem conducts only in one direction i.e vertically. The xylem parenchyma is responsible for storing the prepared food and assists in the conduction of water. Xylem fibres are supportive in function. | 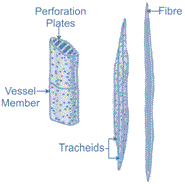 |
| Phloem | It consists of four of elements: sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibres and the phloem parenchyma. Unlike the xylem, phloem conducts in both directions. It is responsible for transporting food from the leaves to the other parts of the plant. Phloem contains living tissues except for fibres that are dead tissues. | 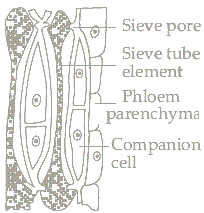 |
Functions of plant tissues
Plant tissues have different functions on the basis of their structure and location and provide mechanical strength to organs.
