Work
When a force acts on an object and the object actually moves in the direction of force, work done by the force is equal to the product of the force and the displacement of the object in the direction of force. If under the constant force F the object displaced through a distance s, then the work done by the force.
W = F*s
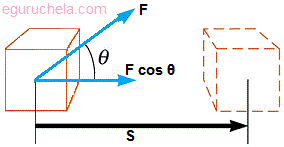
W = F s cosθ
Where,
W = work done by the force.
F = force,
s = displacement caused by the force.
θ = angle between the force vector and the displacement vector.
In other term we can describe to force, if a force acting on a body is able to actually move it through some distance in the direction of the force.
The work done by the force on an object can be positive, negative or zero, depending on the direction of displacement of the object with respect to the force.
If the net work is positive then the velocity of the object is increasing and the net force acts on the object.
If the net force is negative, the velocity of the object decreases and work is done by the object on the other object.
The net work is Zero, when the applied force does not cause displacement(θ = 90 degrees)
The examples of work : Walking up stairs, lifting heavy objects, pulling a sledge and pushing/pulling a trolley.
The SI unit of work : joule (J)
