Specific heat capacity
The heat required to raise unit mass of a substance by unit temperature interval under specified conditions, such as constant pressure: usually measured in joules per kelvin per kilogram. Symbol: cp (for constantpressure) Also called: specific heat.
The specific heat is the amount of heat per unit mass required to raise thetemperature by one degree Celsius. The relationship between heat and temperature change is usually expressed in the form shown below where c is the specific heat. The relationship does not apply if a phase change is encountered, because the heat added or removed during a phase change does not change the temperature.
Q = cm ΔTThe heat capacity of a substance can differ depending on what extensive variables are held constant, with the quantity being held constant usually being denoted with a subscript. For example, the specific heat at constant pressure is commonly denoted CP, while the specific heat at constant volume is commonly denoted CV.
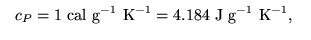
Unit: JKg-1 K-1
Calculating specific heat capacity
E = m × c × θ
