Mean free path
The mean free path is the average distance traveled by a moving particle (such as an atom, a molecule, a photon) between successive impacts (collisions),[1] which modify its direction or energy or other particle properties.
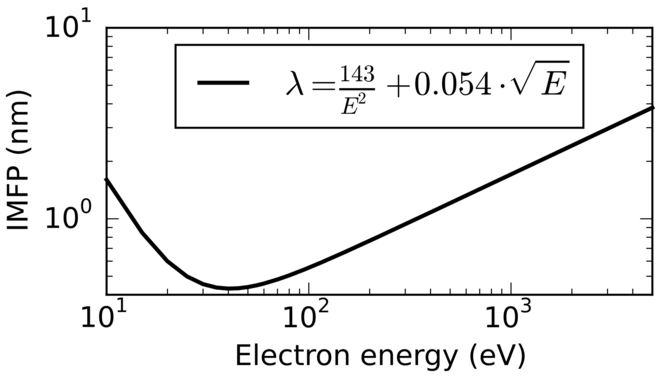
In gamma-ray radiography the mean free path of a pencil beam of mono-energetic photons is the average distance a photon travels between collisions with atoms of the target material. It depends on the material and the energy of the photons:
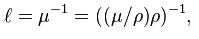
where μ is the linear attenuation coefficient, μ/ρ is the mass attenuation coefficient and ρ is the density of the material. The Mass attenuation coefficient can be looked up or calculated for any material and energy combination using the NIST databases
