Propagation of Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves are waves which can travel through the vacuum of outer space. Mechanical waves, unlike electromagnetic waves, require the presence of a material medium in order to transport their energy from one location to another. Sound waves are examples of mechanical waves while light waves are examples of electromagnetic waves.
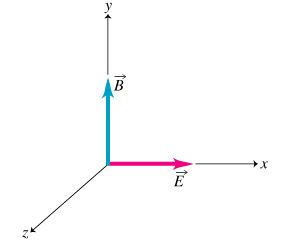
Electromagnetic waves are created by the vibration of an electric charge. This vibration creates a wave which has both an electric and a magnetic component. An electromagnetic wave transports its energy through a vacuum at a speed of 3.00 x 108 m/s (a speed value commonly represented by the symbol c). The propagation of an electromagnetic wave through a material medium occurs at a net speed which is less than 3.00 x 108 m/s. This is depicted in the animation below.
Electromagnetic wave
A wave of energy consisting of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. Radio waves, light waves, and x-rays are electromagnetic waves.