Basic terminologies (Electronic Communication Systems)
The following basic terminologies are used in electronic communication systems:
Signal:
Information converted into an electrical form suitable for transmission is called a signal.
There are two types of signals as follows:
Analog signal and
Digital signal.
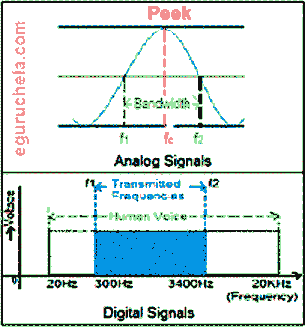
The Analog signals are continuous variations of current and voltage whereas digital signals are those that have discrete stepwise value.
Transducer:
Any device that converts one form of energy into another can be called as a transducer.
In electronic communication system, it mainly refers to a device that converts a physical variable (pressure, sound, force, temperature, etc) into its respective electrical signal and gives it as an output.
A mechanical input is converted into a format which can be understood by the electrical system.
The mouth piece on the phone is a transducer which converts the sound waves into electrical signals.
Attenuation:
The loss of quality and strength of the signal while travelling through the channel/ medium during electronic communication is known as attenuation.
Amplification:
The process of increasing the amplitude of a signal using an electronic circuit is called amplification.
Amplitude refers to the strength of the signal. The electronic circuit used for amplification is called an amplifier.
Whenever the distance between the source and receiver becomes too large such that the signals reaching the receiver are too weak, the addition of an amplifier in between the two can ensure that the receiver receives strong signals.
Demodulation:
The process of extraction of the original information from the modulated signal at the receiver is termed as demodulation. This process is basically the reverse of modulation.
Range:
It is the largest distance between a source and a destination up to which the signal is received with sufficient strength.
Bandwidth:
Bandwidth refers to the frequency range over which an equipment operates or the portion of the spectrum occupied by the signal.
Modulation:
The original low frequency message/information signal cannot be transmitted to long distances because of reasons.
Therefore, at the transmitter, information contained in the low frequency message signal is superimposed on a high frequency wave, which acts as a carrier of the information.
This process is known as modulation. There are several types of modulation.
Types of modulation
1. Amplitude Modulation (AM)
2. Frequency Modulation (FM)
3. Phase Modulation (PM)
Types of electronic communication systems
Coaxial (Wired)
Cable (Wired)
Microwave (Wireless)
Satellite (Wireless)
Cellular (Wireless)
Examples of communication systems
Internet.
Public Switched Telephone network.
Intranet and Extranet.
Television.
