Projectile motion
What is Projectile Motion?
Projectile motion is a form of motion in which an object or particle is thrown near the earth's surface, and it moves along a curved path under the action of gravity only. The only force of significance that acts on the object is gravity, which acts downward to cause a downward acceleration. Because of the object's inertia, no external horizontal force is needed to maintain the horizontal motion. A projectile is launched with an initial horizontal velocity from an elevated position and follows a parabolic path to the ground. Predictable unknowns include the initial speed of the projectile, the initial height of the projectile, the time of flight, and the horizontal distance of the projectile.
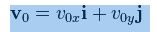
L/T = LT-1 = M0LT-1
Hense,
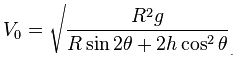
Important Points of Projectile Motion
1. The path of a projectile is parabolic.
2. At the lowest point, the kinetic energy is (1/2) mu2.
3. At the lowest point, the linear momentum is = mu
4. Throughout the motion, the acceleration of projectile is constant and acts vertically downwards being equal to g.
5. The angular momentum of projectile = mu cos Θ × h where the value of h denotes the height.
6. The angle between the velocity and acceleration in the case of angular projection varies from 0 < Θ < 180 degrees.
