Fruit in plant
It is a characteristic feature of the flowering plants. It is a mature or ripened ovary, developed after fertilisation.
If a fruit is formed without fertilisation of the ovary, it is called a parthenocarpic fruit.
Mostly fruit consists of a wall or pericarp and seeds. The pericarp may be dry or fleshy.
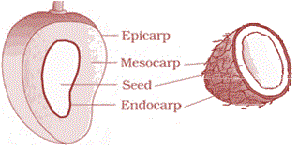
When pericarp is thick and fleshy, it is differentiated into the outer epicarp, the middle mesocarp and the inner endocarp.
| Exocarp | It is the outermost layer which is formed from the outer layer or the epidermis. |
| Mesocarp | Is the second or the middle layer which is often juicy and varies in thickness in different fruits. |
| Endocarp | It is the innermost layer and also is different in different kinds of fruits. |
Types of Fruits
Fruits can be classified following ways as:
In mango and coconut, the fruit is known as a drupe. They develop from monocarpellary superior ovaries and are one seeded.
In mango the pericarp is well differentiated into an outer thin epicarp, a middle fleshy edible mesocarp and an inner stony hard endocarp.
In coconut which is also a drupe, the mesocarp is fibrous.
Imprtance of fruits
The vitamins, minerals, fibre and antioxidants found in fruits and vegetables provide the following benefits:
Strengthen the immune system that helps to fight illnesses
Provide good health and protect against disease in the future.
To ensure the healthy growth and development.
Green fruits help to make bones and teeth strong
