Stem in plant
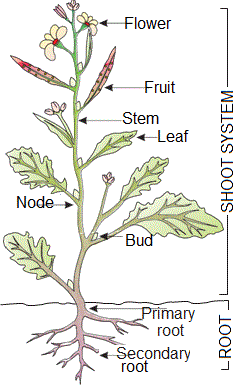
Stem is the vertically growing axis of the shoot system. It is positively phototropic and negatively geotropic in growth. The vertical growth of the stem is maintained by the apical bud. Stem is divisible into nodes and internodes. Leaves are developed on the stem at nodes
Stem is the ascending part of the axis bearing branches, leaves, flowers and fruits.
It develops from the plumule of the embryo of a germinating seed.
The stem bears nodes and internodes.
The region of the stem where leaves are born are called nodes while internodes are the portions between two nodes.
The stem bears buds, which may be terminal or axillary.
Stem is generally green when young and later often become woody and dark brown.
The main functions of a stem
The stem performs the following functions in a plant:
1. The main function of the stem is spreading out branches bearing leaves, flowers and fruits. It supports branches, leaves, flowers, and fruits.
2. Stem transports water and minerals from the roots to the leaves and other parts of plants.
3. Stem transports food from leaves to different parts of the plant.
Some stems perform the function of storage of food, support, protection and of vegetative propagation.
Examples of vegetable stems that we eat
Asparagus, Celery, Rhubarb, Broccoli, Cauliflower, Bamboo shoots, Brussels sprouts, Kohlrabi, Garlic, Onions, Ginger, etc.
Modifications of Stem
Stem are modified to perform different functions.
1. The underground stems of potato, ginger, turmeric, zaminkand, Colocasia are modified to store food in them. They also act as organs of perennation to tide over conditions unfavourable for growth.
1.a. Rhizome: runs parallel to the ground and has nodes, internodes, buds. Examples(Ginger, Banana)
1.b. Tubers: the end part gets swollen as in potato
1.c. Corm: it grows vertically below the ground. Example (Colocasia)
1.d. Bulb: stem is reduced and surrounded by scaly leaves. Examples( Garlic, Onions)
2. The Stem tendrils which develop from axillary buds, are slender and spirally coiled and help plants to climb such as in gourds (cucumber, pumpkins, watermelon) and grapevines.
3. Thorn are Axillary buds of stems may also get modified into woody, straight and pointed thorns. Thorns are found in many plants such as Citrus, Bougainvillea. They protect plants from browsing animals.
4. Subaerial Weak Stem can be as following:
4.a. Offsets :The internode of lateral branches decreases resulting in the rosette of leaves. Examples (Eichhornia, Pistia)
4.b. Suckers :The lateral branches arise from the underground portion of the stem. examples (Chrysanthemum, Banana, Pineapple)
4.c. Runners :The stem run horizontally above the ground and roots arise at nodes. Examples (Grasses, Strawberry)
4.d. Stolon :The lateral branches arise normally but then bend down and touch the soil where the root grows and the new daughter plant arises. Examples (Mint)
5. Aerial modification The stem is completely metamorphosed for various adaptations. Examples (Phylloclade of Xerophytic plants.)
Stem becomes fleshy and green having photosynthetic pigments to prepare food as leaves are reduced to thorns to check water loss by transpiration the examples are Euphorbia, Opuntia.
