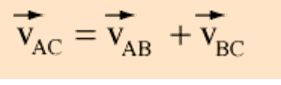Relative velocity
The laws of physics which apply when you are at rest on the earth also apply when you are in any reference frame which is moving at a constant velocity with respect to the earth. For example, you can toss and catch a ball in a moving bus if the motion is in a straight line at constant speed.objects move within a medium that is moving with respect to an observer like the concept of relative motion or relative velocity is all about understanding frame of reference. A frame of reference can be thought of as the state of motion of the observer of some event. For example, if you’re sitting on a lawnchair watching a train travel past you from left to right at 50 m/s, you would consider yourself in a stationary frame of reference.
One must take into account relative velocities to describe the motion of an airplane in the wind or a boat in a current. Assessing velocities involves vector addition and a useful approach to such relative velocity problems is to think of one reference frame as an "intermediate" reference frame in the form: