Refraction and reflection of plane waves using Huygens Principle
Refraction is a test that optometrists and ophthalmologist use to measure a person's refractive error.
A refractive error is when your eye does not bend light coming into your eye properly as it passes through the cornea, the crystalline lens and fluid media to come to a sharp, clear focus onto your retina.
The refraction test will tell the optometrist or ophthalmologist what lens prescription you need in order to have normal 20/20 vision.
Consider the figure given below which shows incident and reflected wave fronts when a plane wave fronts travels towards a plane reflecting surface.
POQ is the ray normal to both incident and reflected wave fronts
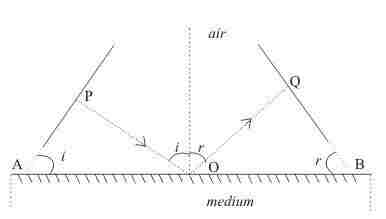
The angle of incidence i and angle of reflection r are the angles made by incidence and reflected rat respectively with the normal and these are also the angles between the wave fronts and the surface as shown in the figure
The time taken by the ray POQ to travel from incident wave front to then reflected one is
Total time from P to Q = t
=PO/v1 + OQ/v1
where,
v1 is the velocity of the wave.
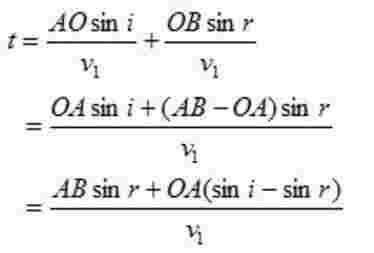
*There can be different rays normal to incident wave front and they can strike plane reflecting surface at different point O and hence they have different values of OA
*Since tome travel by each ray from incident wave front to reflected wave front must be same so, right side of equation (1) must be independent of OA.
This conditions happens only if
(sin i - sin r)=0
or i=r
Thus law of reflection states that angle of incidence i and angle of reflection are always equal
