Atomic Masses and Composition of Nucleus
The mass of an atom is so small that it is inconvenient to express it in kilograms. The unit in which atomic and nuclear masses are measured is called atomic mass unit (amu).
1 amu = 1.67x10-24 g
Avogadro’s number = 6.023 × 1023
Mass of 6.023 × 1023 atoms of C12 = 12 g
Atomic masses can be measured using a mass spectrometer.
The different types of atoms of the same element which exhibit the same chemical properties, but differ in mass are called isotopes.
| Name | Symbol | Electrical charge | Mass (amu) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electron | e | -1 | 0.000549 |
| Proton | p | +1 | 1.00728 |
| Neutron | n | 0 | 1.00867 |
The mass, in amu, of the three particles is given in the table below
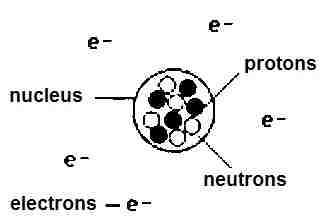
Nucleus
- * The nucleus has the positive charge possessed by the protons. Atomic number is Z. The total charge on an atomic electron is (− Ze) while the charge of the nucleus is (+Ze).
- * The composition of a nucleus is described using the followings terms and symbols.
Z = Atomic number = Number of protons
N = Neutron number = Number of neutrons
A = Mass number = Z + N = Total number of protons and neutrons
Properties of nucleus
The Nucleus is a small, heavy, positively charged portion of the atom and located at the centre of the atom.
All the positive charge of atom are present in nucleus.
Nucleus contains neutrons and protons therefore these particles collectively referred as nucleons.
The radius of nucleus
Mostly nuclear radius range from 1-10 x 10-15 m. This radius is much smaller than that of the atom, atom redius is typically 10-10 m.
It means that nucleus occupies an extremely small volume inside the atom.
Relation between radius of nucleus and mass number
The nuclear radius(R) is one of the basic quantities.
For stable nucleus, the nuclear radius is approximately proportional to the cube root of the mass-number(A) of the nucleus and the nucleons arranged in more spherical configurations.
Mass of nucleus
The nucleus consists of Z protons and N neutrons. therefore the mass of the nucleus will be M (Z + N ).
If a nucleus is assumed to be a simple collection of Z protons and N neutrons, the mass of the nucleus would be just the sum of the masses of these constituent nucleons.
