Cement and its application
Cement is primarily used to produce concrete, the world’s most versatile and durable construction material. Some other applications for cement, however, are now growing in importance.
Cement and its Applications was founded over a hundred years ago and is a privately owned independent trade magazine dealing with the problems of production and application of cement in Russia, in all the newly independent states on the territory of the former USSR and in other countries of the world.
Properties
Highly versatile form of reinforced concrete
It’s a type of thin reinforced concrete construction, in which large amount of small diameter wire meshes uniformly throughout the cross section.
Mesh may be metal or suitable material.
Instead of concrete Portland cement mortar is used.
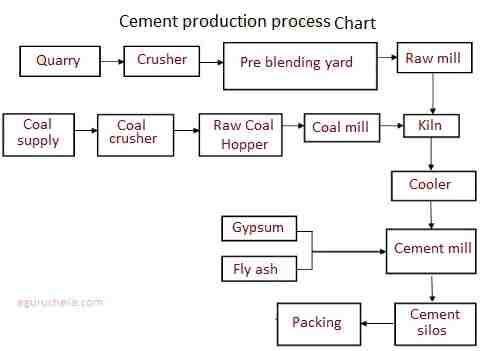
Cement production processes
following steps involve in cement production:Quarrying, Dredging and Digging
By blasting the rocks, limestone and shale is found which is transported to cement plant. The shells are obtained by dredging the ocean floor.
The clay and marl are obtained by digging out of the ground with power shovels. The shell, clay and marl are transported to cement plant.
Grinding
The limestone and shale to be crushed into small pieces. the primary crusher reduces them to the size of a softball. these pieces are then carried to secondary crusher using conveyors.
Blending
The plant chemists analyze the mineral content and proportions of each rock & raw materials to obtain a uniform cement product. The raw materials are then mixed in proper proportions before fine grinding.
Fine Grinding
The fine grinding may be done by wet process or dry process.
The wet process is the older process was used in Europe prior to the manufacture of cement in the United States. This process is used for moist clay and marl.
In wet grinding process, water is added until a slurry (thin mud) forms and the slurry is stored in open tanks where additional mixing is done.
The water may be removed from the slurry before it is burned or the slurry may be sent to the kiln and the water evaporated during the burning.
The dry process is accomplished with a similar set of ball or tube mills and do not add water during the grinding. The dry materials are stored in silos where additional mixing and blending may be done.
Burning
Burning is the key process of making cement. The wet or dry mix is fed into the kiln, which is the largest pieces of moving machinery in the industry.
It is generally having 12+ feet diameter and 500+ feet length made of steel and lined with firebrick. It revolves on large roller bearings.
The materials roll and slide downward for approximately four hours. In the burning zone, where the heat can reach 3,000 F. The materials become incandescent and change in color.
This process emerges is clinker which is round, marble-sized, glass-hard balls which are harder than the quarried rock.
The clinker is then fed into a cooler where it is cooled for storage.
Finish Grinding
Mixed a small amount of gypsum in the cooled clinker which will help regulate the setting time when the cement is mixed with other materials and becomes concrete.
In finish grinding process again there are primary and secondary grinders.
The primary grinders leave the clinker, the primary grinders ground to the fineness of sand and then secondary grinders leave the clinker ground to the fineness of flour as a final product call cement.
Chemical composition of clinker
| Compound | Formula | Shorthand form | % by weight |
| Gypsum | CaSO4.2H2O | CSH2 | 5 |
| Sodium oxide | Na2O | N | } |
| Potassium oxide | K2O | K | }upto 2 |
| Tricalcium aluminate | Ca3Al2O6 | C3A | 10 |
| Tetracalcium aluminoferrite | Ca4Al2Fe2O10 | C4AF | 8 |
| Belite or dicalcium silicate | Ca2SiO5 | C2S | 20 |
| Alite or tricalcium silicate | Ca3SiO4 | C3S | 55 |
Packaging
The final product as cement is packed in bags which are filled by machine. In the United States, one bag of Portland cement contains 94 pounds of cement.
Types of cement and applications
| Types of cement | Composition | Application |
| Hydrographic cement | It is prepared by mixing water repelling chemicals | It has high workability and strength |
| Coloured cement | It is prepared by mixing mineral pigments with ordinary cement. | It has high workability and strength |
| White cement | It is prepared from raw materials free from iron oxide. | It is used for architectural purposes such as pre-cast curtain wall and facing panels. |
| Pozzolanic Cement | It is prepared by grinding pozzolanic clinker with Portland cement. | It is used in marine structures, sewage works, sewage works and for laying concrete under water such as bridges, piers and dams. |
| High alumina cement | It is prepared by melting mixture of bauxite and lime and grinding with the clinker.It is rapid hardening cement with initial and final setting time of about 3.5 and 5 hours respectively | It is used where concrete is subjected to high temperatures, frost, and acidic action. |
| Air Entraining cement | It is prepared by adding indigenous air entraining agents such as resins, glues, sodium salts of Sulphates during the grinding of clinker. | It is used to improve the workability with smaller water cement ratio and to improve frost resistance of concrete. |
| Blast Furnace Slag cement | It is prepared by maintaining the percentage of tricalcium aluminate below 6% which increases power against sulphates. | It is used in construction exposed to severe sulphate action by water and soil in places like canals linings, culverts, retaining walls and siphons |
| Sulphates resisting cement | It is prepared by grinding the clinkers with about 60% slag and resembles more or less in properties of Portland cement | It is used for works economic considerations is predominant. |
| Rapid hardening cement | It is prepared by small percentage of aluminium sulphate as an accelerator and reducing percentage of Gypsum with fine grinding. | It is used in concrete where form work are removed at an early stage. |
| Quick setting cement | It is prepared by increased lime content. | It is used when works is to be completed in very short period and concreting in static and running water. |
| Low heat cement | It is prepared by reducing tri-calcium aluminate. | It is used in massive concrete construction like gravity dams. |
Go to index page
